Showcasing how electricity infrastructure can be adapted to climate change and extreme weather events, RGI has compiled good practices from grid operators across Europe. This is part of RGI’s work with ENTSO-E to contribute to long-term grid planning that considers climate adaptation and resilience aspects.
Climate change and extreme weather events such as floods, strong gusts of winds, storms and heatwaves are increasing across Europe. These developments pose a growing risk to electricity infrastructure, threatening stable and secured electricity transmission that is essential for households, crucial services and the industry. Ensuring that electricity grids remain reliable under changing climate conditions has therefore become a critical priority.
Incorporating climate adaptation aspects into long-term grid planning
European electricity grid planning must consider climate adaptation aspects, according to the revised EU Trans-European Networks for Energy (TEN-E) Regulation. To comply with the new requirements, RGI and ENTSO-E have co-developed a framework that guided a new, quantitative indicator for climate adaptation and resilience measures. This work was developed under ENTSO-E’s Cost-Benefit Analysis (CBA) Methodology, which contributes to assessing long-term grid planning through ENTSO-E’s Ten-Year Network Development Plan (TYNDP). The new indicator is integrated into the 2026 TYNDP update, complementing the existing economic, environmental and system indicators.
Practices strengthening grid resilience in RGI database
To support the development of the framework, RGI and ENTSO-E collected real-world cases on adaptation measures through a survey to electricity transmission and distribution grid operators across Europe. Additional case studies were also gathered through bilateral exchanges and desk research.
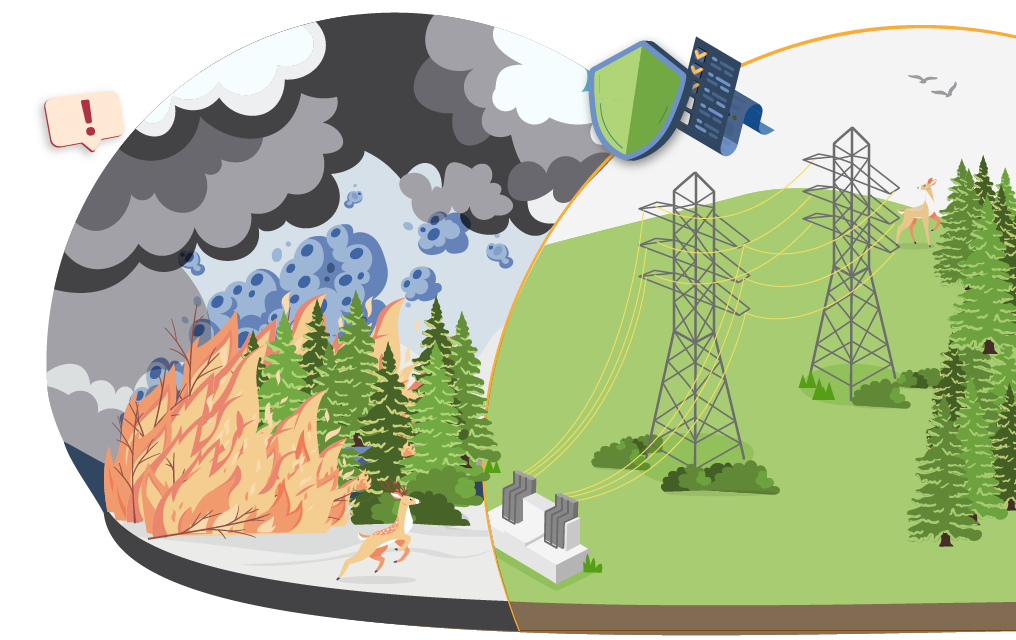
As a result, new practices from across Europe illustrate how grid operators are responding to climate risks in different geographic and climatic contexts, including different approaches, such as:
01
Flood-resilient substations in Ireland, France, Belgium and the Netherlands
02
Undergrounding of power lines in Finland to reduce storm and snow impacts
03
Heat-resilient electricity networks in southern Italy
04
Wildfire prevention and monitoring measures in Portugal
05
Wind and storm risk mapping in Spain
Together, the practices highlight a wide range of technical, operational and planning approaches, from engineering solutions and updated standards to nature-based measures and cross-sector collaboration.
By showcasing practical adaptation measures and their context, these cases support a better understanding of how climate resilience can be integrated into grid planning, assisting a more robust, reliable and resilient energy system in Europe.
Explore the practices
contact
Dr. Andrzej Ceglarz
andrzej[at]renewables-grid.euDirector – Energy Systems

Dr. Ira Shefer
ira[at]renewables-grid.euManager – Energy Systems

Sara Gaçe
sara[at]renewables-grid.euJunior Consultant

more news