This project by the data science and modelling company Artelys shows how grid-enhancing technologies (GETs) can support the integration of increasing volumes of renewables while avoiding delays, high costs and public resistance associated with traditional grid expansion.
Highlights
01
The project uses advanced simulation tools for accurate grid modelling and security analysis.
02
The project analyses how grid-enhancing technologies (GETs) can make better use of existing grids, avoiding costly infrastructure expansion.
03
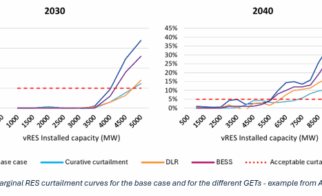
Artelys found the Latvian grid could improve renewable energy integration by up to 40% using grid-enhancing technologies (GETs).
Main Information
This project by the data science and modelling company Artelys uses advanced simulation tools to address the challenge of how to integrate increasing volumes of renewables while avoiding delays, high costs and public resistance associated with traditional grid expansion. The project focuses on deploying cost-effective technical solutions – including curative redispatch, dynamic line rating, FACTS and BESS – strategically to boost renewable energy integration in existing grid infrastructure.
The Latvian TSO AST commissioned Artelys in 2023 to evaluate how much renewable energy the Latvian transmission network could accommodate in the coming decades. The TSO sought to assess which grid-enhancing technologies (GETs) can provide a credible and cost-efficient alternative to costly grid expansion. New transmission lines can take 10 years to build and cost up to one to two million euros per kilometre.
Artelys developed a simulation-based planning methodology combining advanced power system modelling with targeted use of GETs, providing insights into how to boost renewables integration using the technologies. Their analysis showed that innovative grid technologies can improve renewable energy integration in the Latvian grid by up to 40%. The practice is translatable to other regions facing similar challenges with renewable energy integration.
other practices